Network ကို configuration လုပ်တော့မယ်ဆိုရင် network interfaces တွေရဲ့ configuration files တွေကိုပြုပြင်ခြင်းနဲ့လည်းလုပ်လို့ရပါတယ်။ interface configuration file ဆိုတာကတော့ network devices တွေရဲ့ software interfaces တွေကို control လုပ်တဲ့ files တွေကိုပြောတာပါ။ဒီ file တွေကိုများသောအားဖြင့် /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-<name> ဆိုတဲ့နေရာမှာထားပါတယ်။ <name> ဆိုတာကတော့ device တွေရဲ့ interface name ကိုပြောတာပါ။အောက်ကဇယားက variables တွေကတော့ interface တွေကို static (or) dynamic configuration လုပ်တဲ့အချိန်မှာသုံးတဲ့variables တွေပါ။
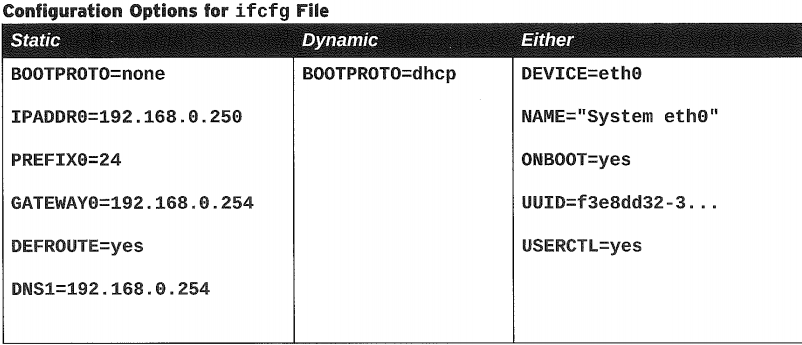
ပုံထဲမှာဆိုရင် ip address, prefix, gateway တွေ၊ DNS အတွက် numbers တွေကို assign လုပ်ပေးထားတာကိုမြင်ရမှာပါ။
configuration file ကို ပြုပြင်ပြီးရင်တော့ nmcli con reload ဆိုတဲ့ command နဲ့ NetworkManager က configuration file ကို read လုပ်အောင်လုပ်ပေးရပါမယ်။အဲ့လိုလုပ်ပြီးတဲ့အခါမှာ interfaces တွေကိုလည်း restart လုပ်ဖို့လိုအပ်ပါသေးတယ်။
[root@demo ~]# nmcli con reload
[root@demo ~]# nmcli con down "System eth0"
[root@demo ~]# nmcli con up "System eth0"
အဲ့ဒါဆိုရင် ကျနော်တို့ exercise လေးလုပ်ကြည့်ကြရအောင်။
၁. root user အနေနဲ့ login ဝင်ပါ။ပြီးရင် serverX နဲ့ desktopX ရဲ့ /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0 ကို IPv4 address 10.0.x.x နဲ့ ip ပေးပါမယ်။
[root@serverX ~]# echo "IPADDR1=10.0.x.1" >> /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
[root@desktopX ~]# echo "IPADDR1=10.0.x.1" >> /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
၂. Network prefix ထည့်ပါမယ်။
root@serverX ~]# echo "PREFIX1=24" >> /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
root@desktopX ~]# echo "PREFIX1=24" >> /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-eth0
၃. အပေါ်မှာပြောခဲ့သလိုပဲ config file ကိုပြင်ပြီးပြီဆိုရင်လုပ်ရမဲ့ step တွေအတိုင်းလုပ်ပါမယ်။
[root@serverX ~]# nmcli con reload
[root@serverX ~]# nmcli con down "System eth0"
[root@serverX ~]# nmcli con up "System eth0"
[root@desktopX ~]# nmcli con reload
[root@desktopX ~]# nmcli con down "System eth0"
[root@desktopX ~]# nmcli con up "System eth0"
၄. On serverX, ကျနော်တို့ configuration လုပ်ခဲ့တဲ့ network address ကို check လုပ်ကြည့်ပါမယ်။
[root@serverX ~]# ip addr
၅. On serverX, ping ကြည့်မယ်။
[root@serverX ~]# ping 10.0.x.2
၆. On desktopX, ip ကြည့်မယ်။
[root@serverX ~]# ip addr
၇. On desktopX, ping ကြည့်မယ်။
[root@serverX ~]# ping 10.0.x.1
##Configuring Host Names and Name Resolution
hostname command ကိုရိုက်ကြည့်မယ်ဆိုရင် system ရဲ့ hostname ကိုမြင်ရမှာပါ။
[root@demo ~]# hostname
demo.example.com
hostname ကိုသိချင်ရင် /etc/hostname file ကိုဖတ်ကြည့်ရင်လည်းသိနိုင်ပါတယ်။
hostnamectl command ကိုအသုံးပြုပြီးတော့လည်း system ရဲ့ hostname ကို modify လုပ်နိုင်သလို hostname status ကိုလည်းကြည့်လို့ရပါတယ်။
[root@demo ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname demo.example.com
[root@demo ~]# hostnamectl status
Static hostname: demo.example.com
Icon name: computer-laptop
Chassis: laptop
Machine ID: d20119f5de9f47beb5aa1123b6332047
Boot ID: c4fd288724b3449a8cd8a0b3c0da7d53
Operating System: Ubuntu 18.04 LTS
Kernel: Linux 4.15.0-23-generic
Architecture: x86-64
[root@demo ~]# cat /etc/hostname
demo.example.com
Configuring Name Resolution
stub resolver က name to ip, ip to name ကို convert လုပ်ပေးပါတယ်။
အရင်ဆုံး /etc/hosts file ကို check လုပ်ကြည့်ပါ။
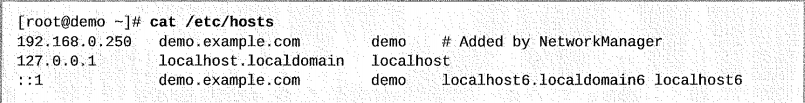
getent hosts hostname command ကိုသုံးပြီးတော့ /etc/hosts file နဲ့ host name resoultion ကို test လုပ်ကြည့်လို့ရပါတယ်။
တကယ်လို့ဘာမှမတွေ့ရဘူးဆိုရင်တော့ stub resolver ကနေတစ်ဆင့် DNS server ဆီကနေရှာပေးပါလိမ့်မယ်။ ဒီအလုပ်ကို /etc/resolv.conf ဆိုတဲ့ config file က လုပ်ပေးပါတယ်။
-
nameserver: DNS server ရဲ့ ip address ကို query အနေနဲ့ရေးထားတာပါ။ဒီနေရာမှာဆိုရင် အနည်းဆုံး 3 ခုလောက်ပေးထားဖို့လိုအပ်ပါတယ်။ဒါမှတစ်ခု down သွားရင်တစ်ခြားတစ်ခုကို backup အနေနဲ့အသုံးပြုလို့ရမှာပါ။
-
search: hostname ကို ရှာဖို့အတွက် search list ပါ။ search list မှာပါတဲ့ domain name တွေက local domain name တွေဖြစ်ပါတယ်။ ဒီ search option ကိုသုံးမယ်ဆိုရင် search list ထဲမှာပါတဲ့ domain တွေကသာ local domain name တွေမဟုတ်ဘူးဆိုရင် network traffic တွေအမျျားကြီးကိုဖြစ်ပေါ်စေမှာပါ။

NetworkManager က connection configuration file ထဲမှာပါတဲ့ DNS setting တွေကို အသုံးပြုပြီးတော့ /etc/resolv.conf file ကို update လုပ်ပါတယ်။ connections တွေကို modify လုပ်ဖို့ nmcli command ကိုပဲအသုံးပြုပါတယ်။
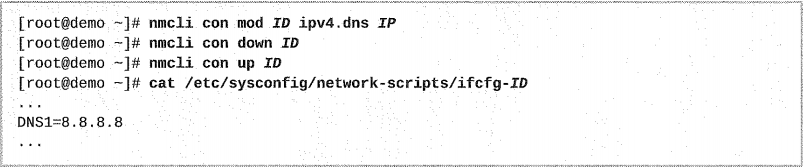
nmcli con mod ID ipv4.dns IP command က ရှိပြီးသား DNS settings တွေကို အသစ်ပေးထားတဲ့ ip lists နဲ့ replace လုပ်ပါတယ်။ ipv4.dns ရှေ့က +/- symbols တွေကို entry ကိုတွေကို add(or)remove လုပ်ဖို့သုံးပါတယ်။
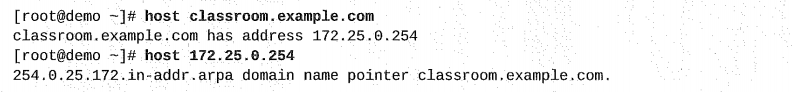
DNS server ရဲ့ connectivity ကို စမ်းဖို့ host HOSTNAME command ကိုအသုံးပြုနိုင်ပါတယ်။
[root@demo ~]# nmcli con mod ID +ipv4.dns IP
ကျနော်တို့ exercise လးလုပ်လိုက်ရင်ပိုပြီးတော့နားလည်သွားမှာပါ။ ၁. System ရဲ့ current hostname ကိုကြည့်ပါမယ်။
[student@serverX ~]$ hostname
serverX.example.com
၂. System hostname ရဲ့ status ကိုကြည့်ပါမယ်။
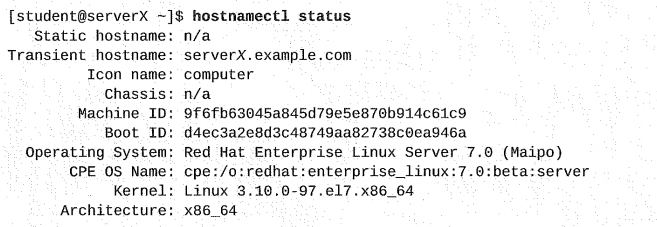
၃. အပေါ်က hostname အတိုင်းမိမိစက်ကို configure လုပ်ပါမယ်။
[student@serverX ~]$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname serverX.example.com
၄. configure လုပ်ထားတာမှန်၊ မမှန်တစ်ချက်ကြည့်မယ်။
[student@serverX ~]$ cat /etc/hostname
၅. hostname ရဲ့ status ကိုကြည့်မယ်။
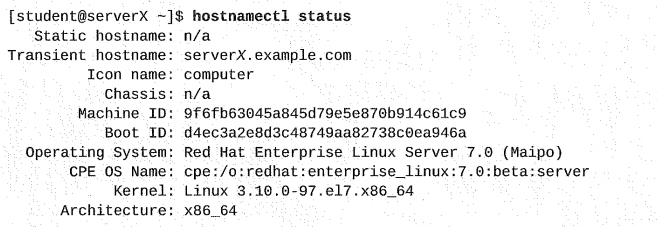
၆. hostname ကို ယာယီ change ကြည့်မယ်။
[student@serverX ~]$ sudo hostname testname
၇. Current hostname ကိုတစ်ချက်ပြန်ကြည့်ကြည့်မယ်။
[student@serverX ~]$ hostname
testname
၈. ယာယီပေးတာဖြစ်တဲ့အတွက် /etc/hostname file ကပြောင်းမှာမဟုတ်ပါဘူး။
[student@serverX ~]$ cat /etc/hostname
serverX.example.com
၉. System ကို reboot ချပါ။
[student@serverX ~]$ reboot
၁၀. reboot ချပြီးပြန်တက်လာရင် hostname ကိုတစ်ချက်ပြန်ကြည့်ကြည့်ပါ။
[student@serverX ~]$ hostname
serverX.example.com
serverX ပဲပြန်ဖြစ်နေပါတယ်။ permanent ပြောင်းချင်ရင်တော့ hostnamectl command နဲ့ပြောင်းရမှာဖြစ်ပါတယ်။